Strategic review approves plan for trial mining at Caula; aim for early revenue from graphite and vanadium products
 Graphite Vanadium Project on track first production mid 2019
Graphite Vanadium Project on track first production mid 2019
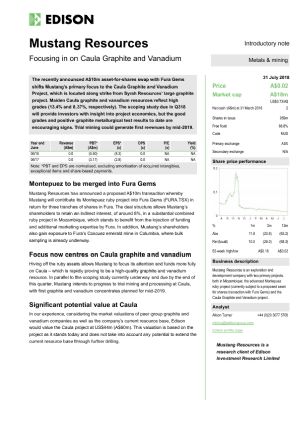
Sydney, Mar 21, 2018 AEST (ABN Newswire) - Mustang Resources ( ASX:MUS) (
ASX:MUS) ( GGPLF:OTCMKTS) is pleased to announce that a strategic review led by new Managing Director Dr Bernard Olivier concludes the Company's Caula Graphite Project in Mozambique could achieve first production by the middle of next year. Dr Evan Kirby, who recently joined the Mustang Board of Directors as a Non-Executive Director and consultant with significant graphite and vanadium experience, assisted Dr Olivier in the review.
GGPLF:OTCMKTS) is pleased to announce that a strategic review led by new Managing Director Dr Bernard Olivier concludes the Company's Caula Graphite Project in Mozambique could achieve first production by the middle of next year. Dr Evan Kirby, who recently joined the Mustang Board of Directors as a Non-Executive Director and consultant with significant graphite and vanadium experience, assisted Dr Olivier in the review.
The strategic review does not form part of the formal Scoping Study, which is set for completion in the June 2018 quarter. The Scoping Study will consider the merits of a full commercial-scale Graphite and Vanadium Project with production levels appropriate to an updated Mineral Resource Estimate, and full consideration of the modifying factors covered in the JORC Code, 2012 Edition.
The key outcome of the review was the recommendation to the Board of Directors of the Company to establish trial mining and processing operations for completion during Q2 2019. The Board of Directors has accepted the recommendation. This recommendation is based on the following considerations:
- Exploration activities have encountered wide intersections of mineralisation with potentially economic graphite and vanadium values.
- Furthermore, the scale and configuration (general topography, width, dip, strike length, and surface outcrop) of the deposit are favourable to trial mining activities ahead of full economic scale exploitation.
- Trial mining and processing will generate detailed technical information for use in formal feasibility studies of full-scale project development. It will also provide product samples for the evaluation by offtake partners, the evaluation of marketing arrangements and the generation of revenue from the sale of the graphite and vanadium products.
- Cost considerations indicate that the Company could finance the establishment of trial mining and processing from its currently available finance facility and planned funding through the current rights issue.
- Work completed to date has shown that Caula could deliver an exceptional combination of both high-grade (13% TGC) mineralisation and graphite products large flakes sizes (~55% large, jumbo and super jumbo) and acceptable purity levels (>95% TGC average in all graphite product flake sizes).
- The vanadium content of the ore could contribute very significant additional value, especially given the structural shift in the vanadium market. First assay results from the recent drilling campaign on Caula returned an average vanadium grade of 0.42% V2O5 over 125m (from 17m to 143m) of the graphitic mineralised zone.
- At the adjacent Montepuez Ruby Project, Mustang has an experienced team with proven capability to obtain exploration and mining permits and the ability to develop trial mining and processing operations. The team will be able to utilise the existing infrastructure and operations camp of the ruby project to assist with graphite project development.
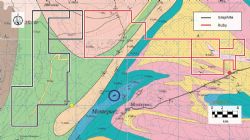
- The recent conversion of exploration licences to mining concessions on the Montepuez Ruby Project that borders the Caula Graphite Project (see Figure 2 in link below) is testimony to these abilities.
- Furthermore, the 200 tph capacity of the processing plant for the Montepuez Ruby Project is ten times larger than contemplated for the trial mining phase of the graphite and vanadium project.
- Completing all permitting, obtaining a mining licence and commencing trial mining operations will strongly differentiate the Caula Project from peer group members who have not progressed so far.
Mustang considers that trial mining and processing operations at Caula could produce both graphite and vanadium concentrates. The vanadium concentrate would either be sold or stockpiled for further processing to high purity vanadium products as part of full-scale development. This expectation is based on reference to the 2014 Vanadium Feasibility Study of Syrah Resources' Balama Graphite Project.
The trial mining development strategy is based on a robust, low-cost mining operation and construction of a processing plant capable of handling approximately 100,000tpa of ore. This scale of operations was decided after discussions with an equipment supplier, followed by preliminary considerations of costs and potential revenues.
The plant will be designed to produce high-grade graphite concentrates as well as vanadium concentrate. In practice, concentrate production rates and qualities will depend on the ore grades fed to the plant, the processing characteristics of the ore, and on plant performance levels achieved. It is anticipated that sales of graphite and vanadium products produced from trial mining will help to secure binding off-take agreements and associated finance required for full-scale project development.
The complex nature of graphite and vanadium extraction means that it is likely that virtually all of the equipment purchased for trial mining will be incorporated into full-scale operations.
Full Scale Graphite and Vanadium Project Development Strategy
Development of a full-scale mining and processing operation will be considered by the Scoping Study. Conditional on a positive outcome of the Scoping Study, a Definitive Feasibility Study (DFS) will be undertaken to serve as a basis for project development and financing. Wherever possible, operational experience from trial mining and processing operations will be incorporated into the DFS.
The throughput and production levels of the full-scale project will be defined by the DFS. In practice, the scale of operations decision will consider factors such as the availability of project finance, and the state of the product markets as well as project specific issues such as the ore reserve and projected operational costs and performance levels.
Background
The Caula Graphite Project represents a unique combination of both high grade and large flake size that distinguishes the project from its peers (see Figure 1 in link below). The Caula project has delivered a maiden JORC Inferred Resource of 5.4Mt at an average grade of 13% TGC (6% cut-off) for more than 700,000 tonnes of contained graphite. The exploration results included exceptionally high-grade intercepts of up to 26% TGC.
The current Caula Mineral Resource estimate is based on five diamond drillholes totalling 484.72 metres and one reverse circulation (RC) drillhole totalling 99 metres. Drillholes were spaced approximately 130 metres apart along a 540 metre strike length. Mustang considers there is strong potential for additional graphite discoveries within the 18km long TEM anomaly.
In addition, initial metallurgical test work has confirmed Caula could yield high percentages of Super Jumbo, Jumbo and Large flakes (~55% from the fresh ore) with carbon content up to 98% through simple flotation (average of 97% C across all size fractions).(see Note 1 below) Oxidised ore has also demonstrated excellent treatment characteristics.(see Note 2 below)
On 16 March 2018 the Company announced the first assay results from its recently completed diamond drilling campaign(see Note 3 below). The assay results returned grades of up to 24.2% Total Graphitic Carbon (TGC) and 1.02% Vanadium (V2O5). Drillhole MODD014 on licence 6678L has an average of 14% TGC within a 125m (from 17m to 143m) mineralised graphitic zone (downhole width). Furthermore, the drill hole has an average vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) grade of 0.42% within a 125m (downhole width from 17m to 143m) mineralised zone (downhole width).
Scoping Study Update
As announced on 5 February 2018(see Note 4 below), the Company has completed the 1,400m diamond drilling campaign on the Caula Graphite Project. The Scoping Study remains on track for completion in Q2 this year. Approximately 1.2 tonnes of diamond drill core, comprising 51 samples from the current drilling program, have been delivered to Nagrom Laboratories in Perth for graphite and vanadium recovery test work. The samples, representing oxide and fresh ore, will be tested both as composites and as individual samples to investigate orebody variability. Multielement analysis of the samples is being performed by SGS South Africa and full results are expected shortly.
Vanadium Economical Potential
The Caula ores are considered to be broadly similar to ore at the nearby Balama Project of Syrah Resources ( ASX:SYR). In July 2014, Syrah published the results of its vanadium scoping study.(see Note 5 below) The outcome of the study was very positive and most of the conclusions drawn have relevance to the Caula Graphite Project. The following points were noted:
ASX:SYR). In July 2014, Syrah published the results of its vanadium scoping study.(see Note 5 below) The outcome of the study was very positive and most of the conclusions drawn have relevance to the Caula Graphite Project. The following points were noted:
- The vanadium in the ore did not report to the graphite concentrate and graphite concentrate samples were below the detection limit for vanadium analysis.
- There was strong correlation between graphite and vanadium grades in the ore.
- Vanadium could be recovered to a concentrate by a combination of froth flotation and wet high intensity magnetic separation (WHIMS). These are well established processing methods commonly applied in the mining and minerals industry.
- A vanadium chemicals plant could be sourced from China where there is extensive experience with vanadium extraction from graphitic and carbonaceous ores. Furthermore, as noted by Syrah, it is likely that the plant would be able to produce high-purity vanadium products that will sell at a significant premium to the industry standard 98% vanadium pentoxide flake.
Worldwide, the major use of vanadium is as an alloying agent in full alloy and high strength low alloy steels. China has recently increased the minimum specification for reinforcing steel used in buildings and as a result, domestic vanadium consumption is expected to increase by 10,000 tonnes per year (Metal Bulletin, August 2017). The vanadium market has already experienced a structural shift, changing China from being a net exporter of vanadium to becoming a net importer of vanadium. The use of vanadium in vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFB batteries), used for large scale energy storage is set to drive a further increase in demand. Consequently, vanadium supplies have tightened, and the price of vanadium has increased sharply over the last two years to current levels of ~US$30,500/tonne, making it the best performing battery metal of 2017(see Note 6 below).
Notes:
1 Refer to ASX Announcement dated 13 Dec 2017 "Caula Graphite Project Metallurgical Results Improved"
2 Refer to ASX Announcement dated 01 December 2017 "Amendment Caula Graphite Project ASX Release of 6 Nov 2017
3 Refer to ASX Announcement dated 16 March 2018 "High Grade Drilling Intersects at Caula Project"
4 Refer to ASX Announcement dated 5 February 2018 "Concept study drilling completed, intersects additional wide shallow zones of graphite at Caula" inclusive of all the JORC Tables listed in the Appendix.
5 Refer to Syrah Resources' ASX Announcement dated 30 July 2014 "Vanadium Scoping Study Finalised".
6 "Best performing battery metal of the year isn't cobalt", Mark Burton. Bloomberg. January 26, 2018.
To view figures, please visit:
http://abnnewswire.net/lnk/UD430XJY
About New Energy Minerals Ltd
 New Energy Minerals Ltd (ASX:NXE) (FRA:GGY) is an ASX listed junior mining company, that recently announced the divestment of the Company's Caula vanadium - graphite project and the Montepuez Ruby project in Mozambique.
New Energy Minerals Ltd (ASX:NXE) (FRA:GGY) is an ASX listed junior mining company, that recently announced the divestment of the Company's Caula vanadium - graphite project and the Montepuez Ruby project in Mozambique.

![abnnewswire.com]()
Related Companies
Social Media
Share this Article

 ASX:MUS) (
ASX:MUS) ( GGPLF:OTCMKTS) is pleased to announce that a strategic review led by new Managing Director Dr Bernard Olivier concludes the Company's Caula Graphite Project in Mozambique could achieve first production by the middle of next year. Dr Evan Kirby, who recently joined the Mustang Board of Directors as a Non-Executive Director and consultant with significant graphite and vanadium experience, assisted Dr Olivier in the review.
GGPLF:OTCMKTS) is pleased to announce that a strategic review led by new Managing Director Dr Bernard Olivier concludes the Company's Caula Graphite Project in Mozambique could achieve first production by the middle of next year. Dr Evan Kirby, who recently joined the Mustang Board of Directors as a Non-Executive Director and consultant with significant graphite and vanadium experience, assisted Dr Olivier in the review.  ASX:SYR). In July 2014, Syrah published the results of its vanadium scoping study.(see Note 5 below) The outcome of the study was very positive and most of the conclusions drawn have relevance to the Caula Graphite Project. The following points were noted:
ASX:SYR). In July 2014, Syrah published the results of its vanadium scoping study.(see Note 5 below) The outcome of the study was very positive and most of the conclusions drawn have relevance to the Caula Graphite Project. The following points were noted:  New Energy Minerals Ltd (ASX:NXE) (FRA:GGY) is an ASX listed junior mining company, that recently announced the divestment of the Company's Caula vanadium - graphite project and the Montepuez Ruby project in Mozambique.
New Energy Minerals Ltd (ASX:NXE) (FRA:GGY) is an ASX listed junior mining company, that recently announced the divestment of the Company's Caula vanadium - graphite project and the Montepuez Ruby project in Mozambique.